主题
Snowflake 算法
算法原理
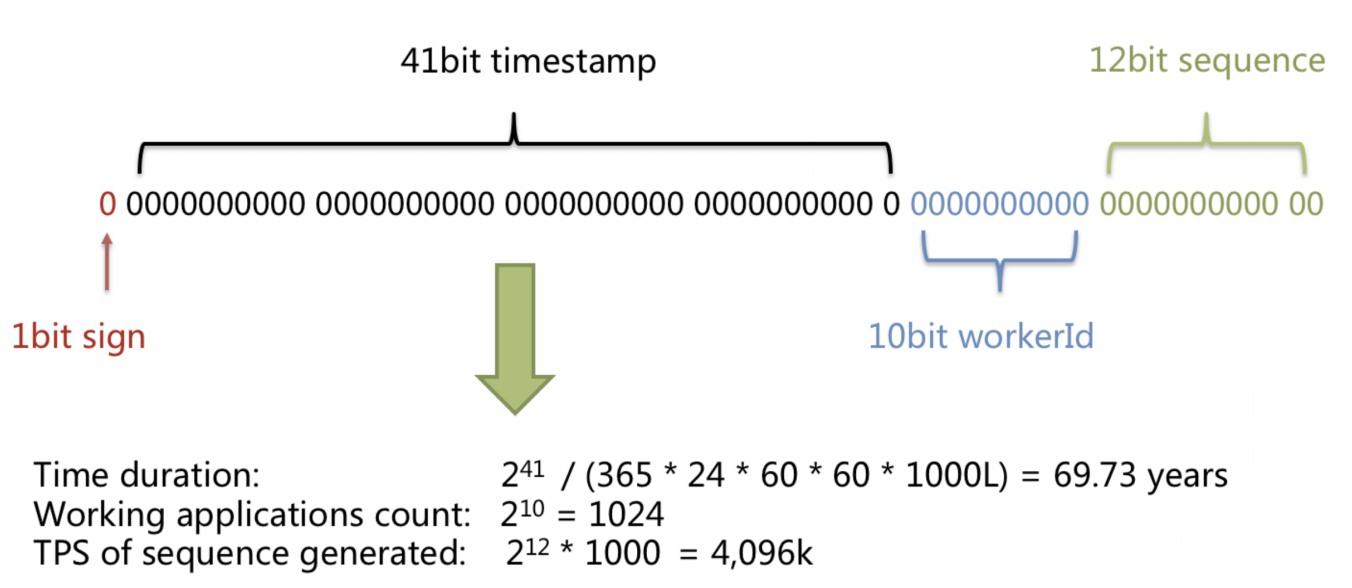
snowflake 算法是 twitter 开源的分布式 id 生成算法,采用 Scala 语言实现,是把一个 64 位的 long 型的 id,1 个 bit 是不用的,用其中的 41 bits 作为毫秒数,用 10 bits 作为工作机器 id,12 bits 作为序列号。
0 - 41位时间戳 - 5位数据中心标识 - 5位机器标识 - 12位序列号
- 1 bit:不用,因为二进制里第一个 bit 为如果是 1,那么都是负数,但是我们生成的 id 都是正数,所以第一个 bit 统一都是 0。
- 41 bits:表示的是时间戳,单位是毫秒。41 bits 可以表示的数字多达
2^41 - 1,也就是可以标识2^41 - 1个毫秒值,换算成年就是表示 69 年的时间。 - 10 bits:记录工作机器 id,代表的是这个服务最多可以部署在 2^10 台机器上,也就是 1024 台机器。但是 10 bits 里 5 个 bits 代表机房 id,5 个 bits 代表机器 id。意思就是最多代表
2^5个机房(32 个机房),每个机房里可以代表2^5个机器(32 台机器)。 - 12 bits:这个是用来记录同一个毫秒内产生的不同 id,12 bits 可以代表的最大数字是
2^12 - 1 = 4095,也就是说可以用这个 12 bits 代表的数字来区分同一个毫秒内的 4096 个(数字 0 到数字 4095)不同的 id。
Java版雪花算法实现
java
/**
* twitter的snowflake算法 -- java实现
*
* @author beyond
* @date 2016/11/26
*/
public class SnowFlake {
/**
* 起始的时间戳
*/
private final static long START_STMP = 1480166465631L;
/**
* 每一部分占用的位数
*/
private final static long SEQUENCE_BIT = 12; //序列号占用的位数
private final static long MACHINE_BIT = 5; //机器标识占用的位数
private final static long DATACENTER_BIT = 5;//数据中心占用的位数
/**
* 每一部分的最大值
*/
private final static long MAX_DATACENTER_NUM = -1L ^ (-1L << DATACENTER_BIT);
private final static long MAX_MACHINE_NUM = -1L ^ (-1L << MACHINE_BIT);
private final static long MAX_SEQUENCE = -1L ^ (-1L << SEQUENCE_BIT);
/**
* 每一部分向左的位移
*/
private final static long MACHINE_LEFT = SEQUENCE_BIT;
private final static long DATACENTER_LEFT = SEQUENCE_BIT + MACHINE_BIT;
private final static long TIMESTMP_LEFT = DATACENTER_LEFT + DATACENTER_BIT;
private long datacenterId; //数据中心
private long machineId; //机器标识
private long sequence = 0L; //序列号
private long lastStmp = -1L;//上一次时间戳
public SnowFlake(long datacenterId, long machineId) {
if (datacenterId > MAX_DATACENTER_NUM || datacenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenterId can't be greater than MAX_DATACENTER_NUM or less than 0");
}
if (machineId > MAX_MACHINE_NUM || machineId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("machineId can't be greater than MAX_MACHINE_NUM or less than 0");
}
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
this.machineId = machineId;
}
/**
* 产生下一个ID
*
* @return
*/
public synchronized long nextId() {
long currStmp = getNewstmp();
if (currStmp < lastStmp) {
throw new RuntimeException("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id");
}
if (currStmp == lastStmp) {
//相同毫秒内,序列号自增
sequence = (sequence + 1) & MAX_SEQUENCE;
//同一毫秒的序列数已经达到最大
if (sequence == 0L) {
currStmp = getNextMill();
}
} else {
//不同毫秒内,序列号置为0
sequence = 0L;
}
lastStmp = currStmp;
return (currStmp - START_STMP) << TIMESTMP_LEFT //时间戳部分
| datacenterId << DATACENTER_LEFT //数据中心部分
| machineId << MACHINE_LEFT //机器标识部分
| sequence; //序列号部分
}
private long getNextMill() {
long mill = getNewstmp();
while (mill <= lastStmp) {
mill = getNewstmp();
}
return mill;
}
private long getNewstmp() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SnowFlake snowFlake = new SnowFlake(2, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << 12); i++) {
System.out.println(snowFlake.nextId());
}
}
}分布式集群需注意
在分布式集群(A/B/C多台机器), 需至少配置一个workId避免和另一台机器生成的id重复, 若服务规模超32台(5位workId上限)可以同时使用 datacenterId (数据中心标识)
MyBatis Plus配置
java
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public IdentifierGenerator identifierGenerator() {
return new DefaultIdentifierGenerator(getWorkerId(), getDatacenterId());
}
// 核心逻辑:优先从环境变量获取,否则IP计算
private long getWorkerId() {
try {
String workerIdStr = System.getenv("WORKER_ID");
if (workerIdStr != null) return Long.parseLong(workerIdStr);
String hostAddress = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
int ipLastSegment = Integer.parseInt(hostAddress.split("\\.")[3]);
return ipLastSegment % 32;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Get workId failed, fallback to default 1");
return 1L; // 兜底策略
}
}
// 数据中心ID同理(略)
}环境变量注入的Docker启动示例:
sh
docker run -e WORKER_ID=2 -e DATACENTER_ID=1 your-service-image