主题
FilterChainProxy过滤器链中的重要过滤器
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
这个过滤器是FilterChainProxy过滤器链的中第一个调用的,先看下它的官方类注释的内容,总结为以下几点:
- 在请求之前,使用从已配置的SecurityContextRepository中获取的认证信息来填充SecurityContextHolder,在请求完成后清除上下文所有者。
- 默认情况下,SecurityContextRepository使用的是HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository作为实现类,有关于HttpSession的配置选项信息请查看HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository。
- 这个过滤器会在每次请求时都会调用,为的是解决servlet容器的兼容性(特别是Weblogic)。
- 这个过滤器必须在任何认证处理机制调用前执行,例如BASIC、CAS认证处理过滤器等都期望在它们执行时能从SecurityContextHolder中获取一个合法的SecurityContext。
- 这个过滤器实质上是对HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository进行了重构,以将存储问题委托给了单独的策略,从而允许在请求之间维护安全上下文的方式进行更多自定义。
首先看下SecurityContextPersistenceFilter的类结构: 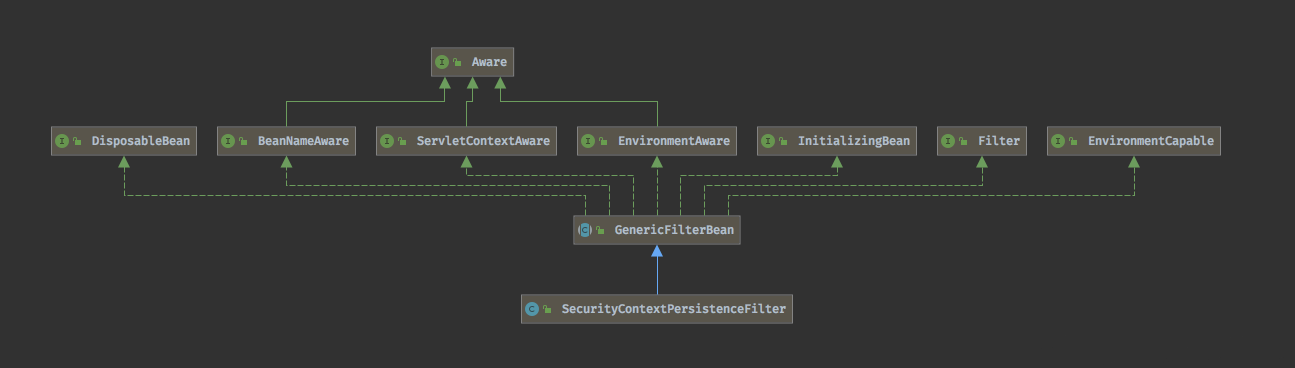 首先它的父类GenericeFilterBean实现了很多接口,其中有三个XXAware的接口,表示的是具备注入XX到GenericFilterBean能力,而这一般都是通过setter来注入XX实现的。
首先它的父类GenericeFilterBean实现了很多接口,其中有三个XXAware的接口,表示的是具备注入XX到GenericFilterBean能力,而这一般都是通过setter来注入XX实现的。
而实现了DisposalbleBean表明了在注销bean时能进行额外的工作,实现InitializingBean表明了能在初始化时进行额外的工作。
源码分析
java
public class SecurityContextPersistenceFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
static final String FILTER_APPLIED = "__spring_security_scpf_applied";
private SecurityContextRepository repo;
private boolean forceEagerSessionCreation = false;
// 默认构造方法,传入HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository
public SecurityContextPersistenceFilter() {
this(new HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository());
}
public SecurityContextPersistenceFilter(SecurityContextRepository repo) {
this.repo = repo;
}
// 过滤核心方法:doFilter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
// 判断请求中是否包含属性:__spring_security_scpf_applied,表示已经调用过SecurityContextPersistenceFilter了
if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) {
// 确保每次请求只调用一次该过滤器
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 为此次请求设置__spring_security_scpf_applied为true,防止下次同样请求再次调用进来时,重复执行以下逻辑
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
// 急切的想要创建Session
if (forceEagerSessionCreation) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if (debug && session.isNew()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly created session: " + session.getId());
}
}
HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request,
response);
// 从HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository中获取SecurityContext安全上下文
SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder);
try {
// 将获取的安全上下文存储到SecurityContextHolder中
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);
// 放过滤器链执行
chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
}
finally {
// 等FilterChainProxy后面所有过滤器链都执行完毕时,进入finally块
// 获取FilterChainProxy调用后的SecurityContext
SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder
.getContext();
// 清除SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
// 将安全上下文存储到HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository中,也就是持久化到Session中
repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(),
holder.getResponse());
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed");
}
}
}
public void setForceEagerSessionCreation(boolean forceEagerSessionCreation) {
this.forceEagerSessionCreation = forceEagerSessionCreation;
}
}从SecurityContextPersistenceFilter类的作用可以看出,它其实就是持久化SecurityContext。
ExceptionTranslationFilter
先看下ExceptionTranslationFilter的类注释,总结为以下几点:
- 此过滤器会处理任何AccessDeniedException和AuthenticationException的异常。
- 此过滤器是必要的,因为它提供了一个桥梁用于连接Java异常和HTTP响应。它仅和维护用户界面有关,而不会执行任何的安全性强制措施。
- 如果此过滤器捕获到了AuthenticationException,该Filter会加载AuthenticationEntrypoint。它允许处理任何从AbstractSecurityInterceptor子类抛出的authentication异常,AbstractSecurityInterceptor的子类即FilterChainProxy中包含的哪些过滤器。
- 如果捕获到了AccessDeniedException,此过滤器会判断当前用户是否是一个匿名用户。如果是匿名用户,则加载authenticationEntryPoint。如果不是匿名用户,则此过滤器会将逻辑代理到AccessDeniedHandler,由其处理接下来的逻辑。
- authenticationEntryPoint指示如果检测到AuthenticationException,则通过调用authenticationEntrypoint的commence方法开始认证过程的处理。需要注意的是,在ExceptionTranslationFilter中的requestCache用于保存身份验证过程中的认证结果,一边可以在用户认证通过后即可检索以及重用,requestCache的默认实现是HttpSessionRequestCache。
小结:ExceptionTranslationFilter的作用即捕获AuthenticationException和AccessDeniedException,并作出相应的处理;对于捕获AccessDeniedException时,如果是匿名用户则去调用authenticationEntryPoint去进行身份验证,如果不是匿名用户则直接抛出AccessDeniedException。
源码分析
先判断看下ExceptionTranslationFilter的成员变量
java
public class ExceptionTranslationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
// AccessDeniedException处理器
private AccessDeniedHandler accessDeniedHandler = new AccessDeniedHandlerImpl();
// 用于进行身份验证的端点
private AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
// 身份认证信任机制,包括判断是否是匿名,判断是否是RememberMe
private AuthenticationTrustResolver authenticationTrustResolver = new AuthenticationTrustResolverImpl();
// 异常分析器
private ThrowableAnalyzer throwableAnalyzer = new DefaultThrowableAnalyzer();
// 将身份认证结果存储在HttpSession中
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
// 消息源转化器
private final MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor();
public ExceptionTranslationFilter(AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint) {
this(authenticationEntryPoint, new HttpSessionRequestCache());
}
public ExceptionTranslationFilter(AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint,
RequestCache requestCache) {
Assert.notNull(authenticationEntryPoint,
"authenticationEntryPoint cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(requestCache, "requestCache cannot be null");
this.authenticationEntryPoint = authenticationEntryPoint;
this.requestCache = requestCache;
}
// 省略
}doFilter源码分析
java
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
// 继续调用下一个过滤器链
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// 尝试去获取SpringSecurityException异常
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
// 转化为运行时异常
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null) {
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
if (ase != null) {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
}
// 处理SpringSecurity异常
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
// Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn't actually happen
// as we've already covered all the possibilities for doFilter
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}java
// SpringSecurityException异常处理的核心逻辑
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// 如果是认证异常
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) {
logger.debug(
"Authentication exception occurred; redirecting to authentication entry point",
exception);
// 开始进行身份认证
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
(AuthenticationException) exception);
}
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) { // 如果是访问拒绝异常
// 尝试从SecurityContextHolder缓存中获取认证结果
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
// 判断认证结果是否是匿名的或者是rememberme
if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) {
logger.debug(
"Access is denied (user is " + (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) ? "anonymous" : "not fully authenticated") + "); redirecting to authentication entry point",
exception);
// 开始进行身份认证
sendStartAuthentication(
request,
response,
chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
messages.getMessage(
"ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
}
else {
logger.debug(
"Access is denied (user is not anonymous); delegating to AccessDeniedHandler",
exception);
// 如果既不是匿名用户也不是rememberme用户,则调用访问拒绝处理器
accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
(AccessDeniedException) exception);
}
}
}java
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 清空缓存中的认证结果,重新进行身份验证
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
// 将认证请求request和响应response存储在session中
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
// 进行身份验证
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}先看下commence的实现类: 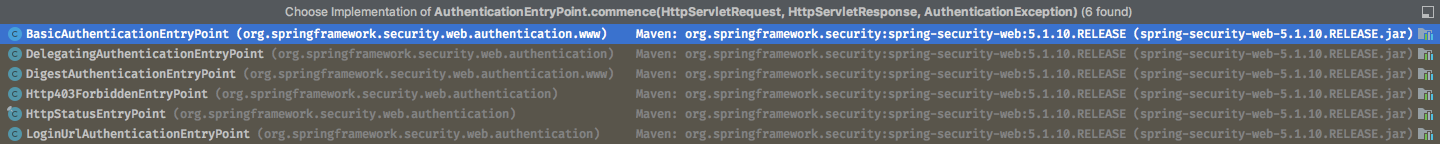
这里这么多实现类,到底调用哪一个呢?这就要看下authenticationEntryPoint注入的什么实现类了,可以将断点打在ExceptionTranslationFilter的构造方法中。 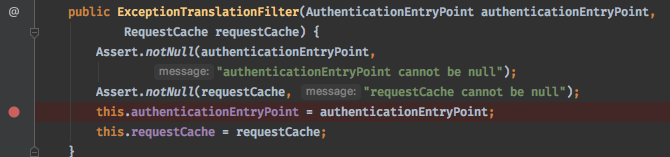
启动项目之后,进入方法调用栈,可以在图中位置看到在进行安全配置类配置时,会调用ExceptionHandlingConfigurer这个配置类的configure方法。 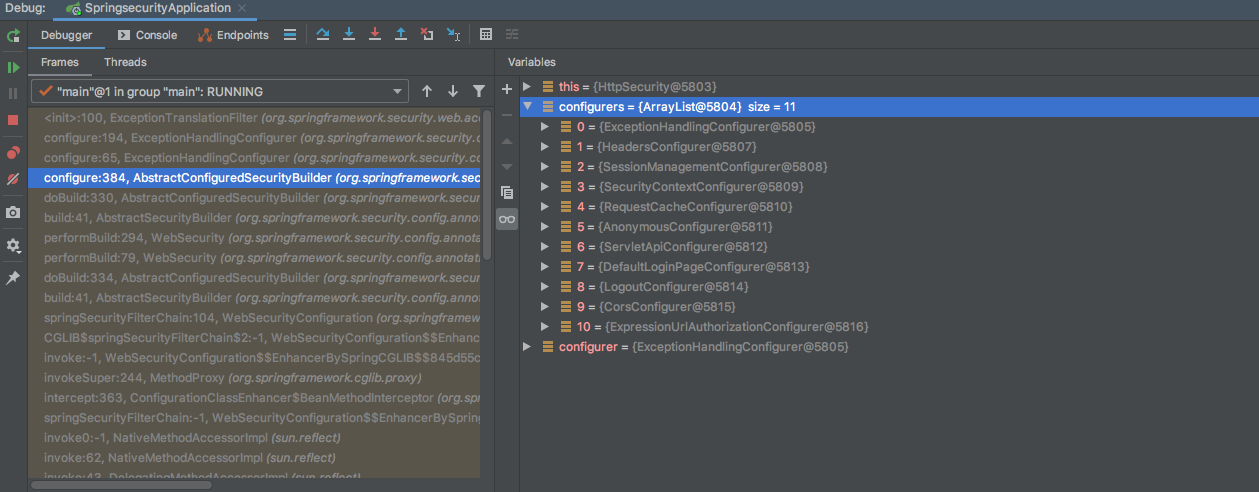
ExceptionHandlingConfigurer
进入其configure方法查看
java
@Override
public void configure(H http) throws Exception {
// 获取authenticationEntryPoint
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = getAuthenticationEntryPoint(http);
// 新建一个ExceptionTranslationFilter对象
ExceptionTranslationFilter exceptionTranslationFilter = new ExceptionTranslationFilter(
entryPoint, getRequestCache(http));
// 或获取访问拒绝处理器
AccessDeniedHandler deniedHandler = getAccessDeniedHandler(http);
exceptionTranslationFilter.setAccessDeniedHandler(deniedHandler);
exceptionTranslationFilter = postProcess(exceptionTranslationFilter);
// 往FilterChainProxy中添加ExceptionTranslationFilter
http.addFilter(exceptionTranslationFilter);
} 可以发现在实例化完ExceptionHandlingConfigurer后,依然没有注入authenticationEntryPoint。所以是在调用configure方法时,去调用getAuthenticationEntryPoint()去获取authenticationEntryPoint。
可以发现在实例化完ExceptionHandlingConfigurer后,依然没有注入authenticationEntryPoint。所以是在调用configure方法时,去调用getAuthenticationEntryPoint()去获取authenticationEntryPoint。
下面接着查看一下getAuthenticationEntryPoint()方法
java
AuthenticationEntryPoint getAuthenticationEntryPoint(H http) {
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = this.authenticationEntryPoint;
// 由于entryPoint为空,所以调用createDefaultEntryPoint去创建entryPoint
if (entryPoint == null) {
entryPoint = createDefaultEntryPoint(http);
}
return entryPoint;
}java
private AuthenticationEntryPoint createDefaultEntryPoint(H http) {
// 如果entryPointMappings为空,则返回Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint
if (this.defaultEntryPointMappings.isEmpty()) {
return new Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint();
}
if (this.defaultEntryPointMappings.size() == 1) {
// 遍历defaultEntryPointMappings,获取其中存储的entrypoint
return this.defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator().next();
}
// 创建DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint这个代理类
DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = new DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint(
this.defaultEntryPointMappings);
entryPoint.setDefaultEntryPoint(this.defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator()
.next());
return entryPoint;
}可以看出,最终返回的就是:Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint 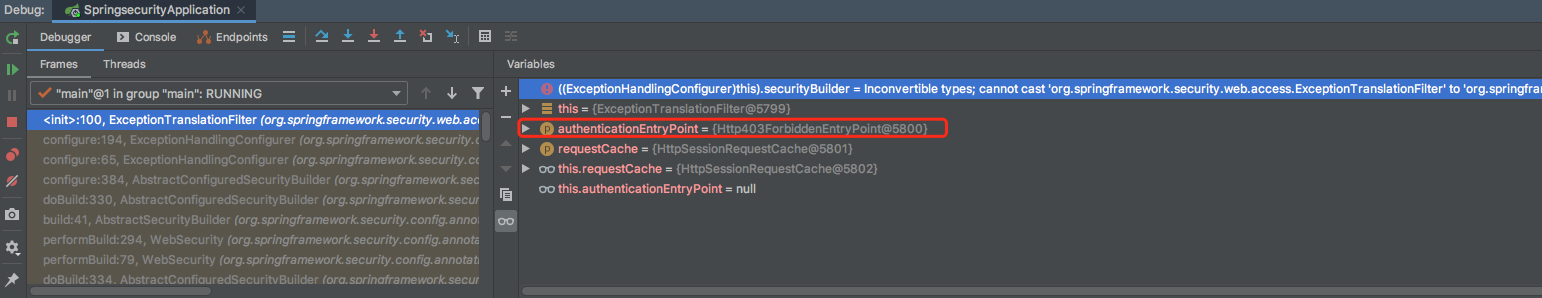
可以看到,HTTP403ForbiddenEntryPiont这个类代码非常少
java
public class Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint.class);
/**
* Always returns a 403 error code to the client.
*/
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException arg2) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Pre-authenticated entry point called. Rejecting access");
}
// 在response响应中添加403 Forbidden,访问拒绝异常
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_FORBIDDEN, "Access Denied");
}
}这里,还讲解一下另外一个类LoginURLAuthenticationEntryPoint的方法commence。
java
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 重定向url
String redirectUrl = null;
if (useForward) {
// 判断下请求协议是否是http
if (forceHttps && "http".equals(request.getScheme())) {
// 获取重定向完整的URL路径
redirectUrl = buildHttpsRedirectUrlForRequest(request);
}
if (redirectUrl == null) {
// 如果重定向地址为空,则获取默认的登录form表单地址;用户可以自定义设置;
String loginForm = determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(request, response,
authException);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Server side forward to: " + loginForm);
}
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(loginForm);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
return;
}
}
else {
redirectUrl = buildRedirectUrlToLoginPage(request, response, authException);
}
// 发送重定向请求
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, redirectUrl);
}LoginURLAuthenticationEntryPoint这个类其实就是重定向到login页面,如果用户不指定login页面,则重定向到默认的login页面。
FilterSecurityInterceptor
FilterSecurityInterceptor 是 Spring Security 中一个核心的过滤器,负责对请求进行访问控制和权限验证。它是 FilterChainProxy 中的最后一个过滤器,主要通过 AccessDecisionManager 进行权限校验。以下是其类注释内容的总结:
- 负责保护 HTTP 请求资源。
- 通过 SecurityMetadataSource 获取当前请求对应的权限配置。
- 利用 Authentication 和 AccessDecisionManager 来判断当前用户是否有权访问资源。
- 如果权限不足,抛出 AccessDeniedException 或 AuthenticationException。
- 提供了一个默认实现类,可以通过自定义扩展 SecurityMetadataSource 和 AccessDecisionManager 来实现定制化。 FilterSecurityInterceptor 的作用可以简单概括为:根据用户身份认证信息和资源的权限配置,判断用户是否有权访问资源,并在无权限时抛出相应的异常。
类结构分析
FilterSecurityInterceptor 继承了 AbstractSecurityInterceptor,并实现了 Filter 接口:
- AbstractSecurityInterceptor: 提供了核心的安全访问控制逻辑。
- Filter: 实现了过滤器接口,能拦截 HTTP 请求。
源码分析
FilterSecurityInterceptor 的核心逻辑体现在其 doFilter 方法中:
java
public class FilterSecurityInterceptor extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter {
private FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource securityMetadataSource;
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource getSecurityMetadataSource() {
return this.securityMetadataSource;
}
public void setSecurityMetadataSource(FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource newSource) {
this.securityMetadataSource = newSource;
}
public Class<?> getSecureObjectClass() {
return FilterInvocation.class;
}
@Override
public SecurityMetadataSource obtainSecurityMetadataSource() {
return this.securityMetadataSource;
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 核心方法:进行权限验证
if (fi.getRequest() != null && fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
return;
}
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
// 调用 AbstractSecurityInterceptor 的权限验证逻辑
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
// 放行过滤器链,继续调用后续过滤器
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} finally {
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
}核心方法解析
invoke(FilterInvocation fi):
- 通过 FilterInvocation 包装当前请求。
- 调用父类的 beforeInvocation 方法进行权限验证。
- 验证通过后调用 doFilter 放行。
- 最后调用 afterInvocation 方法清理上下文。
beforeInvocation:
- 获取 SecurityMetadataSource 中的权限配置。
- 通过 AccessDecisionManager 判断用户是否有访问权限。
- 如果权限不足,抛出 AccessDeniedException。
afterInvocation:
- 在请求完成后进行收尾工作,如清理权限信息或记录日志。
配置分析
FilterSecurityInterceptor 的行为依赖于以下几个组件:
SecurityMetadataSource: 定义资源和权限的映射关系。
通常由 DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource 实现,通过配置文件或注解动态加载。
AccessDecisionManager: 决定用户是否有权访问资源。
默认实现有:
- AffirmativeBased: 只要一个 AccessDecisionVoter 通过即可。
- ConsensusBased: 根据投票数判断。
- UnanimousBased: 所有 AccessDecisionVoter 都通过。
AuthenticationManager: 提供用户身份认证的功能。
工作流程
- 请求进入 FilterSecurityInterceptor: 封装为 FilterInvocation 对象。
- 加载权限配置: 调用 SecurityMetadataSource 获取资源所需权限。
- 权限判断: 调用 AccessDecisionManager 和 AccessDecisionVoter 判断用户是否有权限访问资源。
- 请求放行或拦截: 如果有权限,调用 FilterChain.doFilter 放行。如果无权限,抛出异常。
总结
- FilterSecurityInterceptor 是实际执行权限验证的拦截器,通过 SecurityMetadataSource 获取请求所需的权限,并使用 AccessDecisionManager 判断是否放行请求。
- AccessDecisionManager 是决策管理器,负责评估用户是否有权访问资源,基于投票机制进行权限判断。
- SecurityMetadataSource 提供权限数据源,定义了哪些资源需要哪些权限,从而帮助权限决策。
这三者协同工作,提供了 Spring Security 中强大的访问控制能力。
